Magnetic Forces, Materials, and Devices - Questions With Answers (Short Notes)
01. State Three Ways In Which Forces Due To Magnetic Fields Can Be Experienced?
Answer: There are at least three ways in which force due to magnetic fields can be experienced. The
force can be
- due to a moving charged particle in a magnetic field.
- on a current element in an external magnetic field.
- between two current elements.
02. State The Lorentz Force Equation?
Answer: The Lorentz force equation relates the force acting on a particle with charge Q in the presence of EM fields. It expresses the fundamental law relating EM to mechanics.
F = Q(E + u * B) = m ( du/dt)
Based on the Lorentz force law, the force experienced by a current element Idl in a magnetic field B is
dF = I dl * B
From this, the magnetic field B is defined as the force per unit current element.
03. Define Magnetic Torque?
Answer: The torque T (or mechanical moment of force) on the loop is the vector product of the force F and iho moment arm r.
T = r X F
and magnetic torque is measured in Newton-meters (N • m).Magnetic torque on a current loop with magnetic moment m in a uniform magnetic field B is
T = m * B
04. What Is The Magnetic Dipole Moment?
Answer: The magnetic dipole moment is the product of current and area of the loop; its direction is normal to the loop.
T = m * B
where,T is the magnetic torque
m is the magnetic dipole ( A/m2)
B is the magnetic field
A magnetic dipole is a bar magnet or a small filamentary current loop; it is so called due to the fact that its B field lines are similar to the E field lines of an electric dipole.
05. State The Comparison Between Electric & Magnetic Monopoles & Dipoles?
Answer:
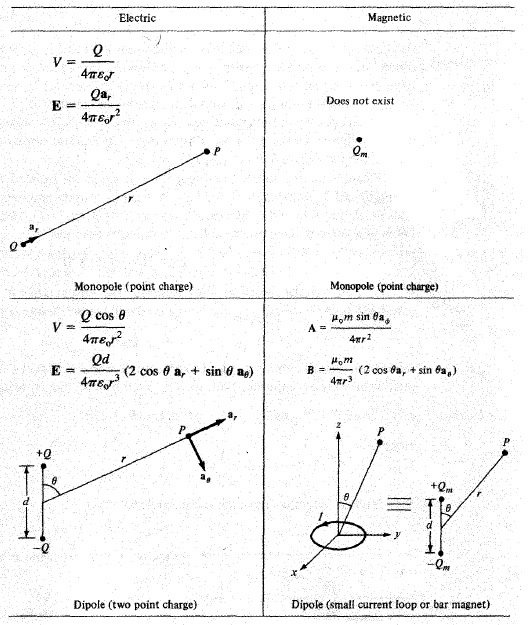


Comments
Post a Comment