Eletromagnetics - Questions With Answers (Short Notes)
1. Define A Uniform Plane Wave.
Answer: In an uniform plane wave the electric and magnetic field vectors both lie in a plane and all such planes are parallel to each other. Also the amplitude and phase of vectors E and H are constant over the planes & they are always normal to the direction pf propagation.
2. State Gauss Divergence Theorem.
Answer: This theorem states that the net flux of a vector field F over any closed surface S is equal to the volume integral of the divergence of that vector field over the volume enclosed by the surface S.
Mathematically it is expressed as:
3. State Stoke’s Theorem.
Answer: This theorem states that the line integral of vector field A around the closed curve forming the periphery of any surface S is equal to surface integral of the curl of that vector field taken over surface S bound by the curve forming periphery of the surface.
Mathematically it is expressed as:
4. What Do You Understand By Displacement Current?
Answer: Maxwell suggested that it is not only the current in a conductor that produces a magnetic field around it, but a time varying electric field in vacuum or in a dielectric also produces a magnetic field. This implies that a changing electric field in vacuum or a dielectric is equivalent to a current which flows as long as the electric field is changing. This equivalent current is known as displacement current.
5. Compare Gauss's Law & Ampere's Law
Answer:
Answer: In an uniform plane wave the electric and magnetic field vectors both lie in a plane and all such planes are parallel to each other. Also the amplitude and phase of vectors E and H are constant over the planes & they are always normal to the direction pf propagation.
2. State Gauss Divergence Theorem.
Answer: This theorem states that the net flux of a vector field F over any closed surface S is equal to the volume integral of the divergence of that vector field over the volume enclosed by the surface S.
Mathematically it is expressed as:
3. State Stoke’s Theorem.
Answer: This theorem states that the line integral of vector field A around the closed curve forming the periphery of any surface S is equal to surface integral of the curl of that vector field taken over surface S bound by the curve forming periphery of the surface.
Mathematically it is expressed as:
4. What Do You Understand By Displacement Current?
Answer: Maxwell suggested that it is not only the current in a conductor that produces a magnetic field around it, but a time varying electric field in vacuum or in a dielectric also produces a magnetic field. This implies that a changing electric field in vacuum or a dielectric is equivalent to a current which flows as long as the electric field is changing. This equivalent current is known as displacement current.
5. Compare Gauss's Law & Ampere's Law
Answer:
- Gauss Law is used to determine electric field due to stationary symmetric charge distributions whereas Ampere's Law is used to evaluate magnetic field due to symmetric steady current distributions.
- Gauss Law involves a surface integral whereas Ampere's Law involves a line integral.
- For applying Gauss law, one needs to construct a Gauss's an surface whereas for applying Ampere's law, one needs to consider a path.
6. Which Equation Shows That Isolated Magnetic Poles Do Not Exist?
Answer: The Maxwell’s second equation ∇ ⋅ B = 0 shows that isolated magnetic poles do not exist.
7. Name The Work-Energy Theorem Of Electrodynamics.
Answer: Poynting's theorem.
8. What Do You Understand By Electromagnetic Waves?
Answer: Electromagnetic waves are coupled to electric and magnetic field oscillations that moves with the speed of light and exhibit typical wave behaviour, i.e.,
Answer: The Maxwell’s second equation ∇ ⋅ B = 0 shows that isolated magnetic poles do not exist.
7. Name The Work-Energy Theorem Of Electrodynamics.
Answer: Poynting's theorem.
8. What Do You Understand By Electromagnetic Waves?
Answer: Electromagnetic waves are coupled to electric and magnetic field oscillations that moves with the speed of light and exhibit typical wave behaviour, i.e.,
- they travel with speed of light
- they are transverse in nature.
- the ratio of electric to magnetic field vector (E/B) in an electromagnetic wave equals to the speed of light
- they carry both energy and momentum.
9. Write Down Maxwell's Equations?
Answer: Maxwell's equations are a set of equations that describe the space and time dependence of the electric and magnetic fields in a medium through partial derivatives.
10. What Is Continuity Equation?
Answer: Continuity equation represents law of conservation of charge. It is expressed as:
Which states that current diverging from an infinitely small volume element is equal to the rate of decrease of charge within that volume.
11. Are All Maxwell’s Equations Independent?
Answer: No. All four Maxwell’s equations are not independent. In fact all four equations are interlinked.
12. What Is Represented By Poynting Vector?
Answer: Poynting vector represents the energy transported by the EM fields per unit time per unit area.
13. What Do You Mean By Intrinsic Impedance?
Answer: The intrinsic impedance or characteristic impedance is the ratio of electric field to the magnetic field intensities, i.e.,
14. State Poynting Theorem.
Answer: Poynting theorem states that the vector product of electric and magnetic field intensity at any point is a measure of rate of flow of energy per unit area at that point, i.e., P = E * H .
15. What Is Poynting Vector?
Answer: Poynting vector is defined as the rate of flow of energy carried by EM waves per unit area of the medium. It is a vector product of electric field and magnetic field vectors. The direction of Poynting vector is in the direction of wave propagation.
Answer: Maxwell's equations are a set of equations that describe the space and time dependence of the electric and magnetic fields in a medium through partial derivatives.
10. What Is Continuity Equation?
Answer: Continuity equation represents law of conservation of charge. It is expressed as:
Which states that current diverging from an infinitely small volume element is equal to the rate of decrease of charge within that volume.
11. Are All Maxwell’s Equations Independent?
Answer: No. All four Maxwell’s equations are not independent. In fact all four equations are interlinked.
12. What Is Represented By Poynting Vector?
Answer: Poynting vector represents the energy transported by the EM fields per unit time per unit area.
13. What Do You Mean By Intrinsic Impedance?
Answer: The intrinsic impedance or characteristic impedance is the ratio of electric field to the magnetic field intensities, i.e.,
14. State Poynting Theorem.
Answer: Poynting theorem states that the vector product of electric and magnetic field intensity at any point is a measure of rate of flow of energy per unit area at that point, i.e., P = E * H .
15. What Is Poynting Vector?
Answer: Poynting vector is defined as the rate of flow of energy carried by EM waves per unit area of the medium. It is a vector product of electric field and magnetic field vectors. The direction of Poynting vector is in the direction of wave propagation.
16. Define Propagation Constant.
Answer: Propagation constant is a complex number and it is given by γ = α + jβ,
where α is attenuation constant and β is phase constant.
where α is attenuation constant and β is phase constant.
17. How Do You Classify A Good Dielectric & A Good Conductor Based On Conduction & Displacement Current Densities?
Answer: For a good dielectric, the ratio of conduction current density (Jc) to displacement current density (Jd) is always less than one in radio frequency range, i.e.,




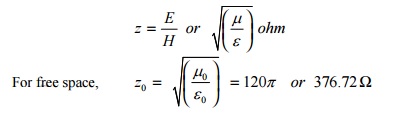



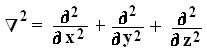
Comments
Post a Comment