Antenna Theory - Solved Numerical's / Problems - ElectroMagnetic Theory...
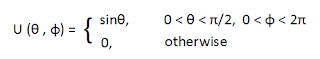
1) An electric field strength of 10 µV/m is to be measured at an observation point θ = π/2, 500 km from a λ/4 monopole antenna operating in air at 50 MHz. (a) What is the length of the dipole? (b) Calculate the current that must be fed to the antenna. (c) Find the average power radiated by the antenna. (d) If a transmission line with Z o = 75 Ω is connected to the antenna, determine the standing wave ratio. --- For Solution CLICK HERE . 2) Calculate the directivity of The Hertzian Monopole. The quarter-wave Monopole. --- For Solution CLICK HERE . 3) A certain antenna with an efficiency of 95% has maximum radiation intensity of 0.5 W/sr. Calculate its directivity when (a) The input power is 0.4 W (b) The radiated power is 0.3 W --- For Solution CLICK HERE . 4) Evaluate the directivity of an antenna with normalized radiation intensity --- For Solution CLICK HERE . 5) Determine the maximum effective area of a Hertzian dipole of length 1