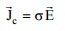ElectroStatics - Questions With Answers (Short Notes)
1. State Stokes Theorem. Answer: The line integral of a vector around a closed path is equal to the surface integral of the normal component of its curl over any surface bounded by the path ∫ H.dl = ∫ ∫ ( ∆ x H ) ds where, H is the Magnetic field intensity 2. State The Condition For The Vector F To Be Solenoidal. Answer: ∆ . F = 0 where, F = A i + B i + C i 3. State The Condition For The Vector F To Be Irrotational. Answer: ∆ x F = 0 where, F = A i + B i + C i 4. Give The Relationship Between Potential Gradient and Electric Field. Answer: E = - ∆V where, E represents Electric Field Intensity and V represents Electric Potential 5. What Is The Physical Significance Of div D ? Answer: The divergence of a vector flux density is electric flux per unit volume leaving a small volume. This is equal to the volume charge density. 6. What Are The Sources Of Electric Field & Magnetic Field? Answer: Stationary charges produce electric field that are