Eletromagnetics - Questions With Answers (Short Notes)

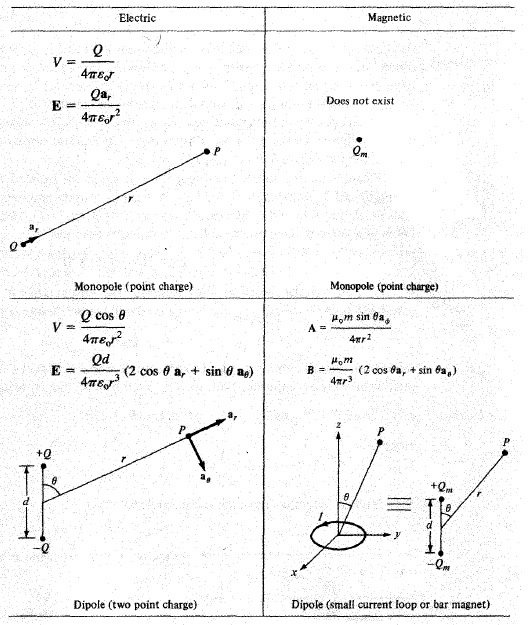
1. Define A Uniform Plane Wave. Answer: In an uniform plane wave the electric and magnetic field vectors both lie in a plane and all such planes are parallel to each other. Also the amplitude and phase of vectors E and H are constant over the planes & they are always normal to the direction pf propagation. 2. State Gauss Divergence Theorem. Answer: This theorem states that the net flux of a vector field F over any closed surface S is equal to the volume integral of the divergence of that vector field over the volume enclosed by the surface S . Mathematically it is expressed as: 3. State Stoke’s Theorem. Answer: This theorem states that the line integral of vector field A around the closed curve forming the periphery of any surface S is equal to surface integral of the curl of that vector field taken over surface S bound by the curve forming periphery of the surface. Mathematically it is expressed as: 4. What Do You Understand By Displacement Current...