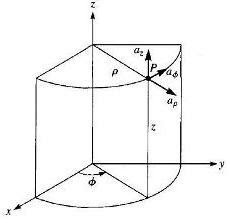
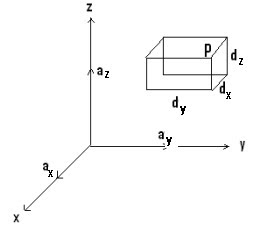
Spherical Coordinate System (r, θ, φ) - Field Theory

Geographers specify a location on the Earth’s surface using three scalar values: longitude, latitude, and altitude. Both longitude and latitude are angular measures , while altitude is a measure of distance . Latitude, longitude, and altitude are similar to Spherical Co-ordinates. Spherical coordinates consist of one scalar value (r), with units of distance, while the other two scalar values (θ, φ) have angular units (degrees or radians). A Vector in Spherical System is represented as (A r A θ , A φ ) or A = A r a r + A θ a θ + A φ a φ Where a r , a θ and a φ are the unit vectors in r, θ and φ direction respectively. The physical significance of each parameter of spherical coordinates: - The value r expresses the distance of the point from origin (i.e. similar to altitude). It is the radius of the sphere. - The angle θ is the angle formed with the z- axis (i.e. similar to latitude). It is also called the co-latitude angle. It is measured clockwise. ...